OpenAI Revenue Surges to $20B as Compute Capacity Triples in 2025
OpenAI reported a major financial milestone in 2025, with annualized recurring revenue surpassing $20 billion. The surge reflects explosive growth in demand for AI services and closely mirrors the company’s rapid expansion of computing infrastructure, according to statements from OpenAI executives.
Key Financial and Infrastructure Results
Revenue Growth
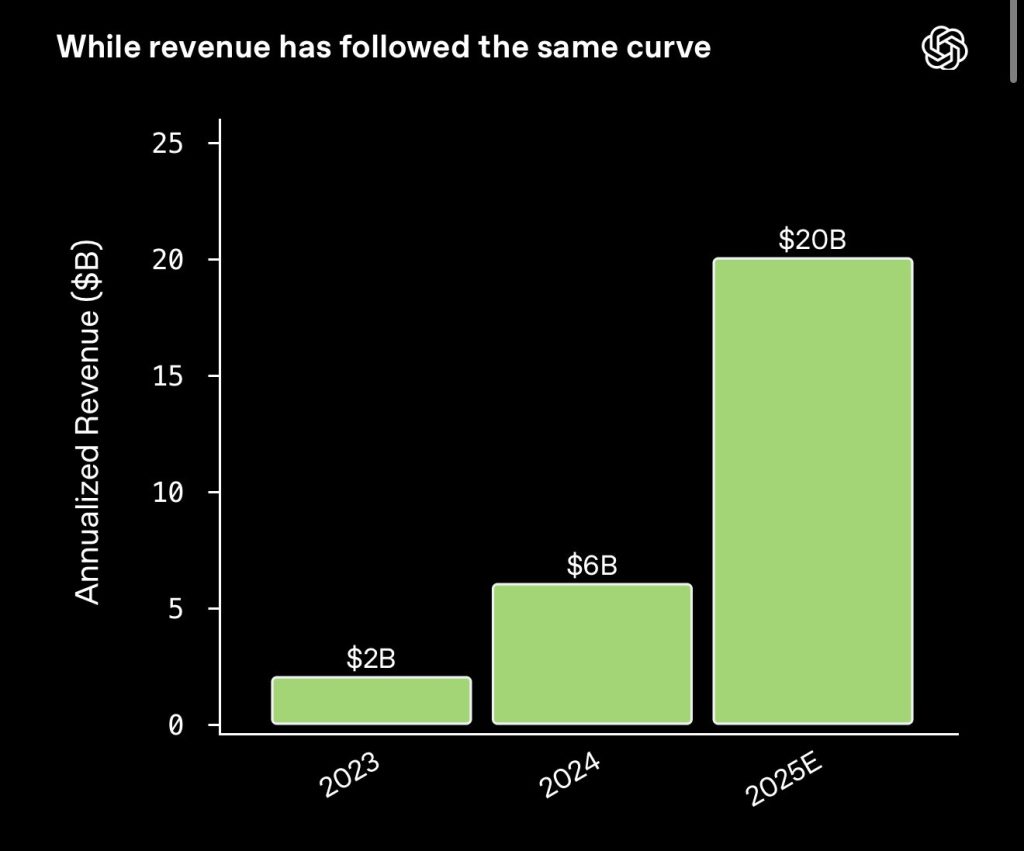
OpenAI’s revenue trajectory over the past three years shows exceptional acceleration:
- 2023: approximately $2 billion
- 2024: around $6 billion
- 2025: more than $20 billion
This represents a tenfold increase in just two years, underscoring the commercial adoption of large-scale AI models across enterprise and consumer markets.
Computing Power Expansion
At the same time, OpenAI significantly scaled its computing footprint:
- 2023: ~0.2 gigawatts
- 2024: ~0.6 gigawatts
- 2025: ~1.9 gigawatts
The company’s total compute capacity has grown nearly three times year over year, keeping pace with rising customer demand for AI inference and training workloads.
Why This Matters
The most striking aspect of the data is the tight correlation between revenue growth and infrastructure expansion. According to Sarah Friar, revenue growth has closely followed the company’s expanding compute footprint, with minimal delay between new capacity coming online and customer utilization.
This is unusual in large-scale infrastructure businesses, where rapid expansion often leads to excess capacity and underutilized assets. In OpenAI’s case, new compute resources appear to be absorbed almost immediately, highlighting the strength of global demand for AI services.
While the figures do not disclose profitability or operating margins, the speed at which demand fills new infrastructure suggests a market willing to pay premium prices for access to advanced AI capabilities.
Outlook for 2026
Looking ahead, OpenAI’s growth trajectory raises both opportunities and risks:
- Continued revenue growth will likely depend on sustained investment in compute infrastructure.
- Rising compute and energy costs could pressure margins if pricing power weakens.
- The close coupling between revenue and infrastructure implies long-term capital expenditure commitments that may be difficult to unwind.
If demand for AI services remains strong, OpenAI could maintain its growth momentum into 2026. However, the sustainability of this model will depend on balancing infrastructure scale, costs, and pricing.
Sources: Chris